Difference between revisions of "Change Management"
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
==== Strategy analysis ==== | ==== Strategy analysis ==== | ||
| + | *Risk assessment - The risk of not managing the people side of change on a particular change is related to the dimensions described in the situational awareness section. Changes that are more 'dramatic' and father reaching in the organization have a higher change management risk. Likewise, organizations and groups with histories and cultures that resist change face higher change management risk. In developing the strategy, overall risk and specific risk factors are documented. | ||
| + | *Anticipated resistance - Many times, after a project is introduced and meets resistance, members of the team reflect that "they saw that reaction coming." In creating the change management strategy, identify where resistance can be expected. | ||
| + | **Are particular regions or divisions impacted differently than others? | ||
| + | **Were certain groups advocating a different solution to the same problem? | ||
| + | **Are some groups heavily invested with how things are done today? <br>Note particular anticipated resistance points depending on how each group is related to the change. | ||
| + | *The identification of any special tactics that will be required for this particular change initiative. The special tactics formalize many of the learnings from the strategy development related to the change and how it impacts different audiences in the organization. Throughout the change implementation, special tactics may need to be revisited and updated | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==== What's next ==== | ==== What's next ==== | ||
Revision as of 14:33, 15 April 2021
| Source: | DataSource |
|---|---|
| Language: | English |
| Topic: | Change Management |
| SubTopic: | ADKAR |
| Last Edit By: | DochyJP |
| LastEdit: | 2021-04-15 |
| Document type: | Training |
| Status: | Active |
| Access: | free |
Introduction
What is Change Management
Context and objectives
When introducing a change to the organization, we are ultimately going to be impacting one or more of the following four parts of how the organization operates:
- Processes
- Systems
- Organization structure
- Job roles
While there are numerous approaches and tools that can be used to improve the organization, all of them ultimately prescribe adjustments to one or more of the four parts of the organization listed above. Change typically results as a reaction to specific problems or opportunities the organization is facing based on internal or external stimuli. While the notion of 'becoming more competitive' or 'becoming closer to the customer' or 'becoming more efficient' can be the motivation to change, at some point these goals must be transformed into the specific impacts on processes, systems, organization structures or job roles. This is the process of defining 'the change'.
Ultimately, the goal of change is to improve the organization by altering how work is done.
Change Management vs Project Management
However, it is not enough to merely prescribe 'the change' and expect it to happen - creating change within an organization takes hard work and structure around what must actually take place to make the change happen. To begin, lets look at the formal definitions of project management and change management - two key disciplines required to bring a change to life. These are two commonly accepted definitions that help us begin to think about these two distinct but intertwined disciplines.
- Project Management : Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements.
Project management is accomplished through the application and integration of the project management processes of initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing.
From PMBOK® Guide, Third Edition
- Change management : Change management is the process, tools and techniques to manage the people-side of change to achieve the required business outcome. Change management incorporates the organizational tools that can be utilized to help individuals make successful personal transitions resulting in the adoption and realization of change.
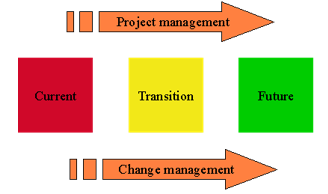
As shown in the figure above, both project management and change management support moving an organization from a current state (how things are done today), through a transition state to a desired future state (the new processes, systems, organization structures or job roles defined by 'the change'). Project management focuses on the tasks to achieve the project requirements. Change management focuses on the people impacted by the change.
Any change to processes, systems, organization structures and/or job roles will have a 'technical' side and a 'people' side that must be managed. Project management and change management have evolved as disciplines to provide both the structure and the tools needed to realize change successfully on the technical and people side.
| Discipline | Process | Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Project management |
|
Tools
|
| Change management |
*Planning for change
|
*Individual change model
|
Separate but integrated in practice
So far project management and change management have been discussed as two distinct disciplines. While separate as fields of study, on a real project change management and project management are integrated. The steps and activities move in unison as teams work to move from the current state to a desired future state.
As an example, think about what activities occur during the planning phase of a project:
On the project management side, teams are identifying the milestones and activities that must be completed. They are outlining the resources needed and how they will work together. They are defining the scope of what will be part of the project and what will not be.
From a change management side, teams begin crafting key messages that must be communicated. They work with project sponsors to build strong and active coalitions of senior leaders. They begin making the case of why the change is needed to employees throughout the organization, even before the specific details of the solution are complete. The most effective projects integrate these activities into a single project plan.
Summary
| Element | Goal or objective |
|---|---|
| "The change" | To improve the organization in some fashion - for instance reducing costs, improving revenues, solving problems, seizing opportunities, aligning work and strategy, streamlining information flow within the organization |
| Project management | To develop a set of specific plans and actions to achieve "the change" given time, cost and scope constraints and to utilize resources effectively (managing the 'technical' side of the change) |
| Change management | To apply a systematic approach to helping the individuals impacted by "the change" to be successful by building support, addressing resistance and developing the required knowledge and ability to implement the change (managing the 'people' side of the change) |
Change Management Process
Change Management Strategy
The change management strategy defines the approach needed to manage change given the unique situation of the project or initiative.
Situational awareness
- Change characteristics - Understanding the characteristics of the change requires you to answer questions like:
- What is the scope of the change?
- How many people will be impacted?
- Who is being impacted?
- Are people being impacted the same or are they experiencing the change differently?
- What is being changed - processes, systems, job roles, etc?
- What is the timeframe for the change?
- Organizational attributes are related to the history and culture in the organization and describe the backdrop against which this particular change is being introduced.
- What is the perceived need for this change among employees and managers?
- How have past changes been managed?
- Is there a shared vision for the organization?
- How much change is going on right now?
- Impacted groups - Developing a map of who in the organization is being impacted by the change and how they are being impacted. Outlining the impacted groups and showing how they will be impacted enables specific and customized plans later in the change management process.
Supporting structure
- The change management team structure identifies who will be doing the change management work. It outlines the relationship between the project team and the change management team. The most frequent team structures include
- change management being a responsibility assigned to one of the project team members or
- an external change management team supporting a project team.
The key in developing the strategy is to be specific and make an informed decision when assigning the change management responsibility and resources.
- The sponsor coalition describes the leaders and managers that need to be on-board for the change to be successful. Starting with the primary sponsor, the sponsor model documents the leaders of the groups that are being impacted by the change. The change characteristics will determine who must be part of the coalition. Each member of the sponsor coalition has the responsibility to build support and communicate the change with their respective audiences.
Strategy analysis
- Risk assessment - The risk of not managing the people side of change on a particular change is related to the dimensions described in the situational awareness section. Changes that are more 'dramatic' and father reaching in the organization have a higher change management risk. Likewise, organizations and groups with histories and cultures that resist change face higher change management risk. In developing the strategy, overall risk and specific risk factors are documented.
- Anticipated resistance - Many times, after a project is introduced and meets resistance, members of the team reflect that "they saw that reaction coming." In creating the change management strategy, identify where resistance can be expected.
- Are particular regions or divisions impacted differently than others?
- Were certain groups advocating a different solution to the same problem?
- Are some groups heavily invested with how things are done today?
Note particular anticipated resistance points depending on how each group is related to the change.
- The identification of any special tactics that will be required for this particular change initiative. The special tactics formalize many of the learnings from the strategy development related to the change and how it impacts different audiences in the organization. Throughout the change implementation, special tactics may need to be revisited and updated
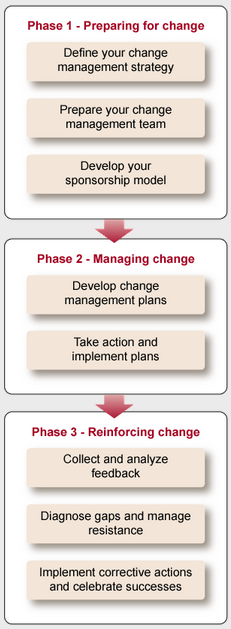
What's next
Prepare for change
Define your change management strategy
Identifying Change Characteristics
Assessing the Organization
Creating a change management strategy
Next steps
Prepare your change management team
Acquiring resources
Assessing team competencies
Preparing the change management team
Develop your sponsorship model
Identifying sponsors and stakeholders
Assessing sponsor competencies
Preparing sponsors
Managing changes
Develop Change Management Plans
Communications Plan
Sponsor roadmap
Coaching plan
Resistance Management Plan
Training Plan
Take action and implement plans
Integrate
Implement
Track
Evaluate
Reinforcing change
Collect and analyze feedback
Listening to employees and gathering feedback
Auditing compliance
Analyzing change management effectiveness
Diagnose gaps and manage resistance
Identifying root causes and pockets of resistance
Developing corrective actions
Enabling sponsors and coaches
Implement corrective actions and celebrate successes
Implementing corrective actions
Celebrating early successes and reinforcing the change
Conducting after-action reviews
Transferring ownership
Toolkit
Change Characteristics Assessment
Change Characteristics Worksheet
Organizational Attributes Assessment
Change Management Strategy
Team Member Competency Assessment
Sponsor Interview Template
Sponsor-ADKAR-Assessment-v6
Primary Sponsor Assessment
Sponsor Assessment Table
Prosci-Sponsorship-Diagram
Communications Plan Template
Change Management Plan Template
Sample Template for Training Supervisors on Change Management
Sample Group Coaching Agenda
Sample Individual Coaching Plan
Communications Plan – Message Guidelines for Employees
Communications Plan – Message Guidelines for Executives
Communications Plan – Message Guidelines for Managers
Communication Plan Template
Sponsor Checklist (Design)
Sponsor Checklist (Implementation)
Sponsor Checklist (Planning and Startup)
Primary Sponsor Plan Template
Change Management Competency Assessment for Managers and Supervisors
Resistance Assessment Worksheet
Training Needs Assessment Template
Training Requirements Template
Change Management Manager
Employee Feedback Assessment
Feedback and Compliance Presentation Template
Corrective Action Plan Template
E-Learning
Concepts and principles in change management 100